Artificial intelligence has transformed from simple, rule-based systems into dynamic technologies capable of mimicking human cognition. Early AI relied on human intervention to adapt, but breakthroughs like artificial neural networks in 2012 marked a shift.
Modern AI types like deep learning enable automation, prediction, and innovation across industries. Understanding these different types of AI helps us navigate its evolving landscape.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the technology that enables machines to mimic human abilities. These include learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. AI systems can process data, identify patterns, and adapt to new information. Examples like self-driving cars and virtual assistants showcase AI’s potential to perform tasks without humans.
These different forms of AI go beyond simple automation. They enable machines to understand human language, recognize images, and create content like text or videos. By breaking down the types of AI, we can better understand how they power the systems we use daily.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs) are key areas within AI that focus on understanding and generating human language. NLP enables machines to analyze, interpret, and respond to text or speech in ways that feel natural to humans. LLMs, which are advanced NLP models trained on vast datasets, take this a step further by generating coherent, contextually relevant responses. These technologies power tools like chatbots, translation services, and content creation platforms, making human-computer interaction more seamless and efficient.
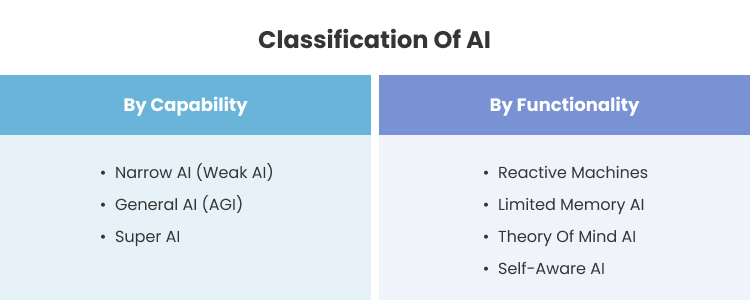
Classification of AI by Capability
AI is classified based on its ability to perform tasks and adapt to new challenges. This categorization shows the shift from specialized systems to more advanced, general ones.
1. Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI, or Weak AI, focuses on performing specific tasks efficiently. It cannot operate outside its programmed functions. Examples include Siri, Alexa, and Netflix’s recommendation algorithms. Narrow AI excels at voice recognition, data analysis, and personalization but lacks flexibility. It is the most common type of AI and drives advancements in automation across industries.
2. General AI (AGI)
General AI refers to machines that can reason and learn in multiple domains, like human intelligence. Unlike Narrow AI, AGI would adapt to new problems without additional programming. Though purely theoretical today, AGI could revolutionize healthcare, education, and robotics. Its development promises groundbreaking innovation but also raises challenges in safety and control.
3. Super AI
Super AI envisions machines that surpass humans in all areas. This includes creativity, reasoning, and emotion.
Super AI, however, remains speculative but has sparked significant debate. It could perform advanced tasks like scientific discoveries and complex decision-making but this raises ethical concerns. What if it surpasses human understanding? There are worries about control, safety, and societal impact.
Classification of AI by Functionality
1. Reactive Machines
Reactive machines perform specific tasks using real-time data. They lack memory and cannot learn from past experiences. For instance, IBM’s Deep Blue chess computer defeated Garry Kasparov by analyzing current board positions. These systems excel at tasks needing immediate analysis. However, they can’t adapt or improve.
2. Limited Memory AI
Limited Memory AI uses past and present data to make decisions. It temporarily stores information but lacks long-term memory. Self-driving cars are a prime example, using sensors and data to navigate safely. These systems continuously adapt to their environment but require regular retraining. Limited Memory AI is widely used in applications needing dynamic responses.
3. Theory of Mind AI
Theory of Mind AI aims to understand emotions, thoughts, and intentions, enabling more personalized interactions. While this advanced concept is still in development, subsets like Emotion AI already analyze voice tones and facial expressions to simulate emotional responses. If fully realized, Theory of Mind AI could transform human-machine relationships. However, its complete implementation remains a theoretical goal for now.
4. Self-Aware AI
Self-Aware AI imagines machines with consciousness and emotions. They could understand their own needs and empathize with humans. The idea is still theoretical but raises ethical concerns about control and regulation. If developed, it might surpass human intelligence and autonomy. This could create opportunities but also major challenges. For now, Self-Aware AI remains a distant possibility.
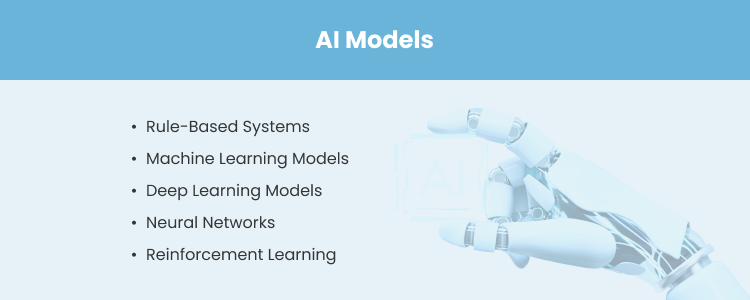
Types of AI Models
AI models are categorized based on their design and operation. They shape how AI systems process data and make decisions. Here are the five primary types:
- Rule-Based Systems. These operate on predefined rules and logic and are ideal for predictable tasks, such as troubleshooting guides and automated customer support.
- Machine Learning Models. They learn patterns from data to make predictions or decisions. They are most common in tasks like fraud detection or recommendation systems, where dynamic data is key.
- Deep Learning Models. These use layered neural networks to process complex data, such as images or speech. Applications include image recognition and natural language processing.
- Neural Networks. Inspired by the human brain, these networks simulate interconnected neurons to identify patterns. They are used in forecasting, classification, and anomaly detection.
- Reinforcement Learning. These focus on learning through trial and error. They are used in robotics and gaming, where systems improve by maximizing rewards for correct actions.
Each of these types of AI models has unique strengths. For example, machine learning and deep learning models improve with data.
Specialized Types of AI in Use Today
Specialized types of artificial intelligence are designed to excel at specific tasks, transforming industries and enhancing daily life. One prominent example is Natural Language Processing (NLP). NLP enables machines to understand and generate human language. It powers chatbots, virtual assistants, and real-time translators.
Another specialized form is Computer Vision. It focuses on enabling machines to understand and analyze visual data like images and videos. This AI type is widely used in facial recognition, medical imaging, and autonomous vehicles. Computer Vision drives innovations in healthcare, security, and retail by spotting patterns in visual inputs.
AI Robotics is another one. It performs precise, adaptive tasks in the real world. Industrial robots streamline manufacturing processes, while surgical robots improve precision in healthcare. Robotics is also crucial in logistics and warehouse management where speed and reliability are essential. By integrating artificial intelligence, robots are becoming more intelligent, safer, and more versatile across various fields.
Emerging Trends in AI Types
Trends like Hybrid AI and Edge AI are pushing AI’s limits. Hybrid AI combines the strengths of multiple models, like machine learning and neural networks, to handle complex tasks more efficiently. For example, hybrid healthcare systems use predictive analytics with diagnostic tools to provide more accurate patient care.
Edge AI, on the other hand, shifts data processing from cloud servers to local devices. This approach improves privacy, reduces latency, and enables real-time responses.
Edge AI is transforming applications like IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and smart home systems. These advancements are making artificial intelligence more responsive, secure, and versatile in real-world scenarios.
How to Differentiate Between Types of AI
AI types can be categorized based on design, purpose, and scope. Design focuses on the underlying architecture, such as rule-based systems or neural networks. Purpose means their intended function. It is either for task-specific automation, like Narrow AI, or for broader adaptability, as in General AI. Scope distinguishes if AI is limited to one task or can learn multiple domains.
To identify an AI type, consider its capabilities and functionality. For instance, Narrow AI excels at tasks like voice recognition. General AI, however, can hypothetically perform any intellectual task. Super AI, still theoretical, would surpass human intelligence. Understanding these differences helps evaluate AI applications and their potential impact across industries.
Use Cases of AI Types in Real Life
Artificial intelligence is transforming healthcare with tools that improve diagnostics and treatment planning. Machine learning analyzes patient data to detect diseases early. Computer vision identifies conditions such as fractures or tumors in medical imaging. NLP-powered chatbots provide quick responses, enabling faster consultations. This reduces the workload on healthcare providers and improves patient care efficiency.
In finance, AI simplifies fraud detection, trading, and customer service. Machine learning detects suspicious patterns in transactions to prevent fraud. Algorithmic trading systems analyze real-time market data and make accurate investment decisions. AI chatbots address account inquiries and provide personalized financial advice. This automation saves time for customers and banks and improves efficiency and security.
AI is also reshaping education and entertainment with personalized and creative applications. Adaptive learning platforms tailor lessons to students’ needs, improving understanding and engagement. AI recommendation engines suggest content on platforms like Netflix and Spotify. They personalize it for users. Generative AI creates music, animations, and virtual characters, revolutionizing creative industries and delivering immersive experiences to audiences worldwide.
Benefits and Limitations of Various AI Types
-
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Benefits: Excels at specific tasks like facial recognition or language translation. It is efficient, reliable, and widely used in industries like healthcare and retail.
Limitations: Limited scope, as it cannot function outside predefined tasks. It also cannot adapt or learn beyond its programming.
-
General AI (AGI)
Benefits: In theory, it could do any intellectual task. It might solve problems and innovate in many areas.
Limitations: The study remains theoretical. AGI development poses major technical, ethical, and safety challenges.
-
Super AI
Benefits: It aims to exceed human intelligence and could lead to major advances in science and technology.
Limitations: It is purely speculative and raises ethical issues. These include a loss of control and potential societal impacts.
-
Reactive Machines
Benefits: Quick decision-making for specific tasks without memory makes them efficient and predictable.
Limitations: They cannot adapt based on past experiences and can only do static, unchanging tasks.
-
Limited Memory AI
Benefits: Retains short-term memory, allowing real-time decision-making. It is widely used in self-driving cars and chatbots.
Limitations: Data retention is temporary, requiring continuous retraining for improved performance. It cannot adapt long-term or learn independently.
These AI types offer immense potential across industries but also face distinct challenges. Narrow AI powers most current applications but is confined to specific tasks. General and Super AI promise limitless possibilities but remain unrealized. Reactive and Limited Memory AI are practical today. But, they need more development to handle complex, adaptive scenarios.
Ethical Considerations in AI Development
As AI systems advance toward Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), ethical concerns grow more urgent. AGI aims to mimic human intelligence, which raises questions about accountability and transparency. For example, who takes responsibility for decisions made by autonomous systems?
Self-aware AI systems and Super AI present even greater challenges. Super AI may create a power imbalance, raising concerns about control and misuse. To address these risks, global efforts, clear governance, and strict ethical guidelines are needed for human safety.
Self-aware AI systems introduce additional ethical challenges. If AI gains consciousness, questions about its rights and status arise. Should a self-aware system have legal protections? These entities might surpass human intelligence, leading to manipulation risks and societal disruption. Addressing these issues also requires global collaboration.
The Future of AI Types
The evolution of AI types promises to reshape industries and daily life. Narrow AI will become more precise, handling specialized tasks with enhanced accuracy. It will drive automation in healthcare diagnostics, personalized education, and intelligent logistics. Meanwhile, Limited Memory AI is expected to advance to enable real-time decisions in dynamic environments.
The future may also see breakthroughs in General AI and Super AI. General AI could handle complex, multi-domain problems, potentially revolutionizing innovation. Super AI, though speculative, might surpass humans. It could solve global issues, like climate change. However, these advancements will require ethical safeguards. Collaborative efforts will be needed to ensure AI types benefit humanity while minimizing risks.
FAQs About Types of AI
What are the main types of AI?
Artificial intelligence can be classified by capability and functionality. Capability-based types include Narrow AI, General AI, and Super AI. Functionality-based types are Reactive Machines, Limited Memory AI, Theory of Mind AI, and Self-Aware AI. Each type varies in scope. Some are single tasks, others are hypothetical systems that could surpass human intelligence.
What is the difference between Narrow AI and General AI?
Narrow AI is task-specific, like voice assistants or recommendation systems. It excels in focused tasks but cannot adapt. General AI, still theoretical, could perform any intellectual task similar to a human. Unlike Narrow AI, General AI would apply reasoning across multiple domains without prior training.
Are there real-world examples of Super AI?
Super AI is currently theoretical and does not exist. It refers to AI systems that would surpass humans in all areas, including creativity and decision-making. While often depicted in science fiction, Super AI remains a concept under exploration by researchers.
How is AI classified based on functionality?
Artificial intelligence functionality is categorized into four types:
- Reactive Machines: Focus on specific tasks without memory.
- Limited Memory AI: Retains temporary data for real-time decisions.
- Theory of Mind AI: Understands emotions and intentions (still under development).
- Self-Aware AI: Hypothetical systems with consciousness and emotions.
What ethical challenges arise with advanced AI types?
Advanced AI types, like General and Super AI, raise concerns about accountability, decision-making, and control. These systems could operate unpredictably, posing risks of misuse or societal disruption. Ethical challenges include:
- Maintaining transparency
- Aligning with human values
- Addressing harm from autonomous decisions
What type of AI is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is a form of Narrow AI. It uses natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to generate human-like text. It can do text-based tasks well but it can’t go beyond its programming. It also lacks the reasoning of General AI.
What is generative AI vs AI?
Generative AI is a type of AI that creates content like text, images, or videos. Examples include ChatGPT and DALL-E. It learns patterns from data to create new outputs. Other AI types focus on tasks like problem-solving or data analysis. Generative AI specializes in creative tasks, while other AI types handle broader functions.
Types of AI: Conclusion
Understanding AI types helps us navigate its influence on industries and daily life. Narrow AI excels at specific tasks, like recommendations. General AI could, in the future, tackle broader, multi-domain problems. Super AI, though theoretical, may surpass human intelligence, raising ethical concerns. By exploring the types of artificial intelligence, we can better appreciate its potential while addressing its challenges.