Artificial intelligence (AI) mimics human intelligence to perform tasks like problem-solving and decision-making. Machine learning (ML), a subset of AI, focuses on learning from data and improving over time. Both technologies are driving innovation. With their growing uses, they are transforming industries and shaping the future of tech.
But how are AI and ML connected? What is the difference between AI and machine learning? And how do these concepts impact organizations today? We’ll break down artificial intelligence vs. machine learning to explain their relationship and critical differences.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to systems that mimic human intelligence. These systems perform tasks like reasoning and problem-solving. AI has been evolving since the mid-20th century. Today, AI powers tools such as voice assistants, autonomous vehicles, and smart devices.
Key subsets of AI include machine learning (ML) and deep learning. ML enables systems to learn from data, while deep learning identifies patterns using neural networks. Natural language processing (NLP) allows machines to interpret and respond to human language. Large language models (LLMs) generate human-like text and are used in tools like chatbots. These technologies streamline processes and improve decision-making across industries.
Applications of AI
- Voice Assistants: AI powers tools like Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant to understand and respond to voice commands.
- Robotics: AI-equipped robots can do complex tasks. These include assembly line work and precision surgeries.
- Medical Diagnostics: AI systems analyze medical data to detect diseases early and recommend personalized treatments.
- Self-Driving Cars: Autonomous vehicles use AI and machine learning to navigate roads and make real-time decisions.
- Predictive Analytics: AI helps businesses forecast trends by analyzing large datasets for patterns and insights.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI. It enables systems to learn and improve from experience without explicit programming. ML uses algorithms to analyze data, identify patterns, and make decisions.
Over time, these systems refine their performance as they process more data. This makes them essential for tasks like predictions, automation, and personalization.
Key concepts in machine learning include supervised learning, in which models learn from labeled data to predict outcomes. Unsupervised learning identifies hidden patterns in unlabeled data without predefined categories. Reinforcement learning trains systems through trial and error, using feedback to improve decisions. These methods drive advancements in AI and machine learning, transforming industries worldwide.
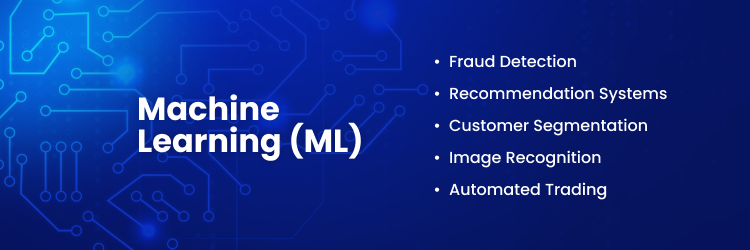
Applications of Machine Learning
- Fraud Detection: Machine learning algorithms analyze transaction patterns to identify and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Recommendation Systems: ML powers personalized recommendations on platforms like Netflix and Amazon, enhancing user experience.
- Customer Segmentation: Businesses use ML to group customers for targeted marketing. They base this on behavior, preferences, or demographics.
- Image Recognition: ML models process and analyze images to detect objects, faces, or text in applications such as security and healthcare.
- Automated Trading: Financial markets leverage ML to execute trades based on real-time data and predictive analytics.
Differences Between AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are connected but distinct concepts. AI mimics human intelligence to perform tasks like reasoning and decision-making. ML focuses on learning from data and improving performance over time. AI offers a broad framework for intelligent systems. ML specializes in specific tasks by finding patterns in data.
Artificial intelligence simulates human intelligence to handle tasks requiring logic and reasoning. It aims to create adaptable systems that can perform complex activities. Machine learning, on the other hand, trains models to analyze data and make predictions. AI has a broad focus, while ML refines specific processes through data-driven learning techniques.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Goal: Mimics human intelligence to solve problems and make decisions.
- Scope: Broad, covering technologies like robotics, machine learning, and NLP.
- Data Usage: Works with structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
- Functionality: Replicates reasoning, perception, and self-correction.
- Applications: Used in autonomous vehicles, voice assistants, and analytics.
- Approach: Utilizes logic, decision trees, and adaptive systems.
Machine Learning (ML)
- Goal: Enables systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time.
- Scope: Focuses on solving specific problems like predictions and classifications.
- Data Usage: Uses primarily structured and semi-structured data.
- Functionality: Learns patterns from data using algorithms and statistical models.
- Applications: Powers fraud detection, recommendation engines, and customer segmentation.
- Approach: Employs supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning techniques.
Benefits of Using AI and ML Together
- Wider Data Ranges: AI and ML can process large datasets, leading to better insights and more accurate predictions.
- Faster Decision-Making: Automated processes powered by AI and ML reduce delays and help make decisions in real-time.
- Improved Efficiency: These technologies handle complex problems accurately and require less human intervention.
- Seamless Integration: AI and ML combine analytics to improve system performance and offer holistic insights.
How Are AI and Machine Learning Related?
Artificial intelligence is the framework for intelligent systems, and machine learning lets them improve their performance. Together, AI and ML create adaptive and efficient technologies.
Machine learning is essential for advancing artificial intelligence. It includes techniques like supervised learning and deep learning. These methods support broader AI applications, such as robotics and natural language processing.
ML enhances AI capabilities by analyzing data and learning from patterns. This collaboration leads to smarter systems and innovations across industries.
Advantages of AI and Machine Learning

- Enhanced Efficiency: AI and ML streamline processes, reducing the time and effort needed for complex tasks. This helps organizations focus on strategic goals.
- Reduced Human Error: These technologies minimize mistakes by automating critical operations. This improves accuracy in sensitive areas like finance and healthcare.
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks: Routine tasks are handled efficiently, freeing up human resources for strategic work. This boosts overall productivity and innovation.
- Better Data-Driven Decisions: AI and ML analyze large datasets, providing insights that improve decision-making. Businesses can adapt faster to changing trends.
- Scalability: Systems powered by AI and ML can scale operations seamlessly as businesses grow. They adjust to handle increased workloads effectively.
- Innovation in Industries: These technologies drive innovation by enabling solutions like personalized recommendations and predictive analytics. They open doors to entirely new possibilities.
Limitations of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence faces several challenges that limit its use. Ethical concerns, such as privacy issues, raise questions about its impact. Dependence on large datasets can make it less effective without quality data. Interpretability is another issue, as it is often unclear how AI systems make decisions. This reduces trust in areas like healthcare or finance.
Machine learning also has its own challenges. Bias in training data can lead to unfair results. High computational requirements make it costly for smaller businesses.
Overfitting is another problem, where models work well on training data but fail with new data. These limitations highlight the need for careful planning when using AI and machine learning.
Applications of AI and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming industries by solving complex problems and driving innovation. These technologies automate tasks, improve decision-making, and enhance efficiency. They process vast amounts of data to uncover patterns and insights that help address critical challenges. Their adaptability makes them essential for tackling diverse issues across various fields.
The flexibility of AI and ML allows them to excel in both emerging and established sectors. In renewable energy, they optimize resources and forecast energy demands. In healthcare, they improve diagnostics and personalize treatments. Retail and finance, established industries, benefit from better customer experiences and predictive analytics.
Specific sectors have embraced AI and machine learning to achieve groundbreaking advancements. Healthcare, manufacturing, e-commerce, finance, and telecommunications are leading the way. These industries use AI and ML to boost efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver innovative solutions. Their use in these sectors shows that tech can adapt and drive progress.
- Healthcare: AI and ML enable early disease detection through data analysis. They also help develop personalized treatment plans and discover new drugs.
- Manufacturing: These technologies optimize production processes through predictive maintenance. They also ensure quality control by detecting defects in real time.
- E-commerce: AI and ML power recommendation systems to personalize customer experiences. They also assist with inventory management and dynamic pricing strategies.
- Finance: Machine learning models improve fraud detection and risk management. AI also supports algorithmic trading for better investment strategies.
- Telecommunications: Network optimization and predictive analytics improve service quality. AI chatbots also improve customer support experiences.
Key Industries Leveraging AI and ML
- Healthcare and Life Sciences: AI and ML enable predictive diagnostics to identify diseases early. They support personalized treatments tailored to individual patients and assist in drug discovery. Automated tools also benefit patient management, improving care delivery.
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance helps reduce downtime by identifying potential equipment failures. Quality control is enhanced through real-time defect detection. Automation streamlines production lines, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- E-commerce and Retail: AI-powered recommendation systems provide personalized shopping experiences. Inventory management ensures stock availability and reduces waste. Customer segmentation helps retailers create targeted marketing campaigns.
- Financial Services: Fraud detection systems identify unusual transaction patterns to prevent fraud. Risk management tools assess and mitigate potential economic losses.
- Telecommunications: Network optimization improves connectivity and reduces downtime. AI chatbots enhance customer service experiences. Service personalization ensures tailored offers and solutions for individual users.
Future Trends in AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are evolving rapidly. Emerging trends are shaping their future impact across industries. Generative AI, like ChatGPT, creates content, images, and code. This is transforming creative fields and automating complex tasks. Ethical AI is becoming a priority, focusing on fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Advancements in natural language processing (NLP) are improving human-like interactions. These trends are setting new benchmarks for AI’s role in society.
The future of machine learning includes significant strides in model interpretability. This will make AI systems easier to understand and trust. Better explainability will show users how decisions are made. This will boost adoption in healthcare and finance.
ML is also expected to grow into new areas, like environmental monitoring and space exploration. These advancements will expand AI and machine learning and drive innovation across industries.
How to Choose Between AI and Machine Learning for Your Business
Choose artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) based on your business goals. AI is ideal for tasks that require systems to simulate human intelligence. Examples include speech recognition and decision-making.
ML excels at analyzing data, identifying patterns, and building predictive models. Consider the quality of your data and your available technical resources. Decide if your focus is on automation or gaining data-driven insights.
Assess your core business needs and scalability goals carefully. ML models may be sufficient for automating repetitive tasks or improving efficiency. AI systems are a better fit if you need skills like natural language understanding or reasoning.
Scalability is also key—ensure the solution can grow with your business. Consult with data scientists to create a tailored approach that meets long-term objectives.
FAQs about Machine Learning vs AI
What is the difference between artificial intelligence and machine learning?
Artificial intelligence (AI) mimics human intelligence for tasks like decision-making. Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that uses data to train systems to improve over time. While AI focuses on broad intelligence, ML specializes in tasks like predictive modeling.
Can you use AI without machine learning?
Yes, you can use AI without machine learning. Rule-based and expert systems are examples of AI that don’t rely on data-driven learning. However, combining AI and machine learning improves flexibility for tasks like speech recognition.
Which is better: AI or machine learning?
The choice depends on your goals. AI is better for tasks requiring broad decision-making. ML is ideal for analyzing data and improving specific outcomes. Businesses with large datasets often benefit from ML models. AI systems are suitable for handling reasoning tasks.
How do AI and machine learning work together?
AI and machine learning complement each other. AI sets the framework for reasoning and decision-making. ML builds models that analyze data and improve accuracy over time. For example, an AI system may use ML algorithms for better predictions.
Are machine learning and AI the same?
No, they are not the same. Machine learning is a part of artificial intelligence (AI), including robotics and natural language processing. ML focuses on creating data-driven models that adapt and learn.
Is ChatGPT an AI or machine learning?
ChatGPT is an AI system that uses machine learning techniques. It relies on predictive modeling and neural networks to generate human-like text, making it both an AI application and an ML product.
Can AI replace machine learning?
No, AI cannot replace machine learning. AI depends on ML to learn from data and improve decision-making. Without ML, many AI systems would lack adaptability and predictive capabilities.
What are the main challenges in using AI and machine learning?
Challenges include ethical concerns, such as data privacy and algorithm bias. AI and machine learning require robust computer systems and large datasets. You also need skilled computer science professionals to develop and manage these technologies.
Conclusion: Understanding the Difference Between AI and ML
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are distinct but connected. AI mimics human intelligence to solve complex problems. ML focuses on learning from data to improve specific outcomes. Together, they drive innovation in industries like healthcare and finance. Understanding their roles is essential for leveraging their potential and advancing technology.





















