Keeping cryptocurrency safe is a top concern for investors. Cold wallets offer a secure way to store digital assets by keeping private keys offline, away from hackers and cyber threats. This storage method helps prevent unauthorized access and reduces security risks.
This article explores what a cold wallet is, how it works, and why it is crucial for protecting your crypto.
What Is a Cold Wallet?

A cold wallet is a secure way to store crypto assets by keeping them completely offline. It does not connect to the internet or interact with smart contracts. This separation strengthens security by blocking malware, phishing attempts, and cyber threats. Keeping wallets disconnected also prevents illegal approvals that could lead to asset loss.
Many people mistake cold wallets for hardware wallets, but they are not always the same. Cold wallets come in different forms; not all hardware wallets offer true cold storage.
Security Features of Cold Wallets
Cold wallets offer several security features that make them an attractive option for cryptocurrency users. These features include:
- Offline storage: Cold wallets store private keys offline, making them inaccessible to hackers and malware. This offline storage significantly reduces the risk of cyberattacks.
- Physical protection: Cold wallets are often stored in a physical device, such as a hardware wallet, which provides an additional layer of protection against physical damage or loss. These devices are designed to be tamper-resistant and durable.
- Access control: Cold wallets use various access control techniques, such as passphrases, recovery phrases, PIN codes, and biometric verification, to ensure that only authorized users can access the wallet. This multi-layered security approach helps prevent unauthorized access.
- Secure chip storage: Many cold wallets use dedicated secure elements, such as tamper-resistant chips, to store private keys and protect them from both software and physical threats. These secure chips add an extra layer of security, ensuring that private keys remain safe even if the device is compromised.
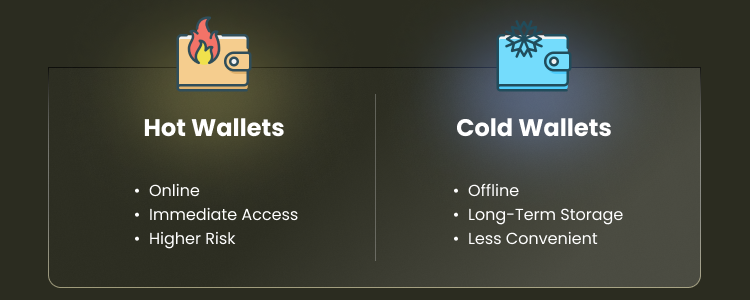
Cold Wallet vs. Hot Wallet
Hot wallets connect to the internet, allowing faster transactions but increasing security risks. Cold wallets differ from hot wallets by highlighting their contrasting connectivity to the internet. While cold wallets remain offline for enhanced security, hot wallets are accessible online, which makes them more susceptible to cyber threats. Cold wallets keep assets offline, preventing cyberattacks and AI attacks. While users need extra steps to access funds, they gain stronger protection against theft and unauthorized transactions.
The distinctions between hot and cold wallets are significant. Hot wallets store keys online and are more convenient for transactions, while cold wallets offer greater security by keeping keys offline.
In 2025, hackers stole over $1.5 billion from Bybit in one of the largest crypto heists to date. They targeted the exchange’s cold wallet, proving that cold storage reduces risks but does not eliminate them. Exchanges that move funds frequently face higher risks, while individual users who store assets offline have stronger protection.
How Does a Cold Wallet Work?
A cold wallet operates by keeping cryptocurrency transactions completely offline. Unlike hot wallets, which process transactions directly, cold wallets require users to sign transfers manually. This extra step ensures that private keys never interact with the internet. By staying disconnected, the wallet effectively blocks remote hacking attempts.
When a user initiates a transaction, they first create a request on an online device. The request is then transferred to the cold wallet, where the private key signs it in an offline environment. Since the wallet remains disconnected, the key stays safe from cyber threats. This process ensures that no sensitive data is exposed during transaction signing.
Once signed, the transaction moves back to the online device. It is then broadcast to the blockchain network for validation via an internet-connected device. This air-gapped process guarantees that private keys remain secure even if the online system is compromised.
Types of Cold Wallets
Each type of cold wallet offers different security levels and accessibility. Some focus on long-term storage, while others balance security with usability. Choosing the right one depends on how often users need access to funds and the level of protection required.
Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets are considered the most reliable cold wallets due to their secure technology and ability to keep private keys offline. To authorize transactions, users enter a PIN or confirm actions manually. Some models use QR codes instead of USB connections, adding extra security. Popular brands like Ledger, Trezor, and Coldcard provide encryption and offline signing, making them one of the safest storage options.
Paper Wallets
A paper wallet involves printing or writing down private keys on paper. Since it never connects to the internet, it remains safe from malware and cyberattacks. However, users must store it carefully to avoid damage or loss. Offline tools like WalletGenerator.net help generate them securely. This method is best for long-term storage without frequent transactions.
Offline Software Wallets
Offline software wallets store private keys on air-gapped devices, keeping them away from online threats. Users sign transactions offline and transfer them to an online device for broadcasting. This method offers high security but requires technical expertise to set up and manage. Electrum and Armory provide trusted solutions for those preferring software-based cold storage.
Deep Cold Storage
Deep cold storage keeps private keys in ultra-secure locations, such as vaults, safes, or metal backups. Institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals use this method to secure large crypto holdings. Cryptosteel allows users to engrave keys onto fireproof metal plates, protecting them from damage. Though highly secure, deep cold storage makes accessing funds difficult.
Sound Wallets
Sound wallets encrypt private keys as audio files stored on CDs, vinyl records, or other media. Users need specialized software to decode and retrieve funds. While this method adds an extra security layer, audio degradation and data loss make it less practical. Unlike other cold storage options, sound wallets require careful handling to stay functional.
Benefits of Using a Cold Wallet
- Better Security: Keeps private keys offline, blocking hackers and malware.
- Reliable for Long-Term Storage: Protects large crypto holdings without online exposure.
- Full Ownership of Funds: Users manage their funds without relying on exchanges.
- Safe from Exchange-Related Risks: Not affected by exchange hacks, shutdowns, or withdrawal limits.
- Minimal Exposure to Digital Threats: No online authentication or system vulnerabilities.
Risks of Using a Cold Wallet
Cold wallets offer strong security but come with risks. Losing access to a hardware or paper wallet can result in permanent fund loss. Unlike online wallets, there are no password resets or recovery options. Physical damage from fire or water can also make retrieval impossible without a backup.
Protecting the backup seed phrase is crucial. If someone gains access, they control the wallet. Losing it means funds cannot be recovered. Cold wallets also require manual signing and transfers, making them less convenient for frequent transactions.
In 2022, $2.7 billion was lost to smart contract hacks, a 1,250% increase from 2020. Hackers exploit online wallet vulnerabilities and decentralized applications. Cold wallets prevent this by keeping private keys offline, and protecting funds from unauthorized access.
Why Do You Need a Cold Wallet?
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly common. If a traditional bank account is compromised, the bank can refund the lost or stolen money. However, if a cryptocurrency wallet is compromised, the tokens cannot be recovered or reimbursed.
Cryptocurrency is not insured or backed by a government or institution, and transactions on a blockchain cannot be reversed. Therefore, it is essential to use a cold wallet to protect your private keys and ensure the security of your cryptocurrencies.
By keeping your private keys offline, a cold wallet provides a robust defense against hacking attempts and unauthorized access, safeguarding your investments in the volatile world of digital currencies.
What Are the Challenges of Cold Wallets?
Cold wallets provide strong security, but users must manage private keys carefully. Accessing funds requires extra steps, making transactions less convenient for frequent users. Since cold wallets stay offline, transferring assets takes longer than online wallets.
Setting up a cold wallet requires technical knowledge. Users must understand private keys, recovery phrases, and secure storage methods. Without proper setup, they risk misplacing credentials, which leads to permanent loss. Learning to store and back up a cold wallet safely ensures long-term security.
Another challenge is cost. Hardware wallets require an upfront investment, and high-quality devices are expensive. Paper wallets cost less but remain fragile and need careful storage. Choosing a secure cold wallet solution requires balancing cost, ease of use, and long-term protection.
How to Use a Cold Wallet Securely
- Set Up the Wallet Properly: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to initialize the cold wallet. Keep it offline during setup to ensure private keys remain secure.
- Store Private Keys Offline: Do not digitally save private keys or recovery phrases. Writing them on paper or engraving them on a metal backup helps prevent data loss.
- Use a Strong Seed Phrase: Generate a 12- or 24-word seed phrase and store it securely. Sharing it with others can put funds at risk.
- Encrypt Backups: If you create a digital backup, use strong encryption to prevent unwanted access. Keep multiple copies in secure locations, such as a locked safe.
- Verify Transactions Offline: Always review transaction details on the wallet’s screen before confirming. This ensures accuracy and prevents mistakes.
- Regularly Test Recovery Methods: Periodically check that your backup seed phrase works correctly. This helps you regain access if the wallet is lost or damaged.
- Keep the Wallet Secure: Store hardware wallets in a fireproof and waterproof environment. Using multiple wallets for redundancy adds another layer of protection.
Best Practices for Using a Cold Wallet
To get the most out of your cold wallet, follow these best practices:
- Use a reputable cold wallet provider: Research and choose a reputable cold wallet provider that offers robust security features and a user-friendly interface. Trusted brands like Ledger and Trezor are known for their reliability and security.
- Keep your private keys secure: Never share your private keys with anyone, and make sure to store them in a secure location. Consider using a fireproof and waterproof safe for added protection.
- Use a strong passphrase: Choose a strong and unique passphrase to protect your cold wallet, and make sure to store it in a secure location. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or common words.
- Regularly update your wallet software: Regularly update your wallet software to ensure that you have the latest security patches and features. Keeping your software up-to-date helps protect against new vulnerabilities.
- Verify transactions carefully: Always verify transactions carefully before confirming them, and make sure to use a secure internet connection. Double-check the recipient address and transaction details to avoid costly mistakes.
Are Cold Wallets Completely Safe?
Cold wallets offer strong protection, but mistakes can still lead to fund loss. Human error is the biggest risk, especially when users lose their seed phrases or fail to back up their wallets properly. If access is lost, there are no password resets or recovery options.
Users should encrypt backups, keep private keys offline, and regularly test recovery options to maximize security. While cold wallets reduce exposure to cyber threats, proper precautions are necessary to prevent loss or theft. Following security best practices ensures both safety and accessibility for long-term asset protection.
How Cold Wallets Protect Against Theft
Since cold wallets do not interact with the internet, they remain safe from hacking attempts and software vulnerabilities. This isolation helps prevent cyber threats that commonly affect online wallets.
Encryption adds an extra layer of security for wallet backups. Many hardware wallets come with encrypted chips that prevent tampering. Storing backup phrases in metal wallets or secured offline storage helps protect against data loss. Keeping private keys in a safe, well-protected location ensures the highest level of asset security.
Do You Really Need a Cold Wallet?
Not everyone needs a cold wallet. It’s best for investors with large holdings who prioritize security.
Smaller investors may prefer software wallets for easy access. Some offer multi-signature protection, combining offline and online security.
Choosing a wallet depends on investment size, security needs, and accessibility. Hardware wallets cost $50–$200+, but they provide strong protection. Hot wallets are more convenient for daily use.
Cold Wallets vs. Hot Wallets: What’s the Difference?
Hot wallets store private keys online for fast transactions but are vulnerable to hacks. Cold wallets store private keys offline, away from internet-connected devices, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized access by hackers and enhancing overall security. The best choice depends on security needs, accessibility, and investment size.
Hot Wallets: Advantages & Disadvantages
Hot wallets are internet-connected, making them ideal for quick access. They support instant transfers and work well for traders. Popular types include mobile, desktop, and web wallets.
However, storing private keys online increases risk. Hot wallets are prone to hacking, malware, and phishing attacks. Even with encryption and multi-factor authentication, they remain vulnerable if a device or exchange is compromised.
FAQs About Cold Wallets
Can I Use a Cold Wallet for Daily Transactions?
No. A cold crypto wallet is designed for secure asset management, not frequent transfers. Each transaction requires manual signing, making it slower than a hot wallet.
How Often Should I Back Up My Cold Wallet?
Back up at setup and when adding assets. Store multiple copies securely—never online. Use a secret recovery phrase to regain access if the wallet device is lost.
Can Cold Wallets Be Hacked?
Not remotely, since they are an offline wallet. However, if someone accesses your private keys printed or seed phrase, they can steal your funds.
What is the best cold wallet for beginners?
Hardware wallets are the most popular cold wallets due to their security and user-friendly interface. Choose a wallet provider with strong encryption and regular hardware wallet firmware updates.
How do I choose between different cold wallets?
Options include hardware devices, sound wallets (store audio files of encrypted keys), paper wallets (physical documents with a paper wallet address), and deep cold storage wallets. Each has pros and cons.
Can I store smart contracts in a cold wallet?
No. A cold wallet works by keeping funds stored offline, making it incompatible with smart contracts, which require an internet connection.
Are old cold wallets safe to use?
It depends. Some old wallet options lack security updates. Always check your hardware wallet’s firmware and avoid outdated USB sticks or compromised physical wallet methods.
How do I access a cold wallet?
Most cold wallets safe require signing transactions offline, then transferring the data to a wallet app via a QR code or USB stick before broadcasting it.
Does Coinbase Wallet offer cold storage?
No, Coinbase Wallet is a hot and cold hybrid, meaning it connects to the internet but can work with external cold storage wallets like hardware wallets for better security.
Cold Wallets: Our Final Thoughts
Cold wallets keep public and private keys offline, protecting cryptocurrency from cyber threats. They are best for long-term investors and those holding large amounts of crypto. While transactions take extra steps, the security benefits make them worth it for those prioritizing fund protection.
Choosing the right cold wallet depends on security needs and accessibility. Popular cold wallets include hardware wallets with encryption, offline signing, and backup features. Paper wallets offer simplicity but risk loss or damage. Deep cold storage provides maximum security for institutional investors.
To stay secure, store backup seed phrases offline in safe locations. Test recovery methods regularly and use tamper-proof storage to prevent loss. Cold storage isn’t for everyone, but it remains the most reliable option for those needing strong security and full control.